Selective Voice Sensitivity (Mizophonia)
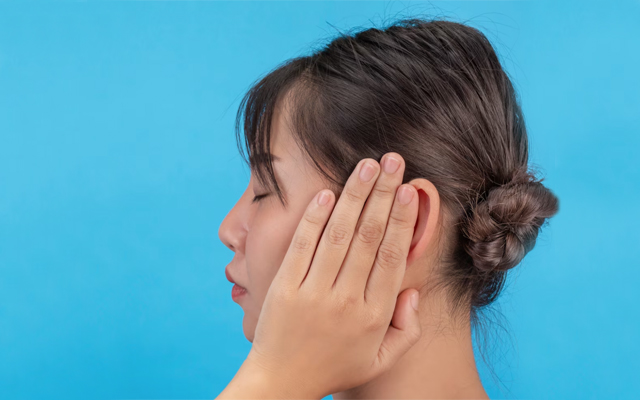
Mizophonia is a disease that is being seen in more and more people every day. In addition to being known as hypersensitivity to sounds, it is also referred to as selective sound sensitivity syndrome in some literatures.
People with this disease are disturbed by sounds such as mouth smacking, chewing gum, whistling, breathing, nail cutting, snoring, coughing, talking, eating and brushing teeth.
Often found in people with ear sensitivity, it can be accompanied by obsessive-compulsive disorder, anxiety or depression. Mizophonia is more common in individuals with high levels of stress and anxiety.
It is often seen in women and adolescents between the ages of 9 and 12. There is no drug treatment for this disease, but if anxiety and depression accompany the disease, the person can be supported with medication.
The persistence of external voices gradually reduces the patience of the individual with these voices and the individual may lose control.
Symptoms of this disease are as follows; a feeling of tightness in the chest when there is noise, preference for night time rather than day time due to the silence of the night, inability to stand in the same places with children and babies, closing the ears or avoiding when certain sounds are heard, and a nervous, irritable attitude.
Although there is no definitive treatment method in terms of treatment, it has been observed that positive results are obtained with voice therapy accompanied by psychologists. Several forms of therapy are recommended for treatment, including cognitive behavioral therapy, voice therapy, retraining therapy and lifestyle changes.
Hashtags
mizophonia voice ocd
Categories
Actual Other