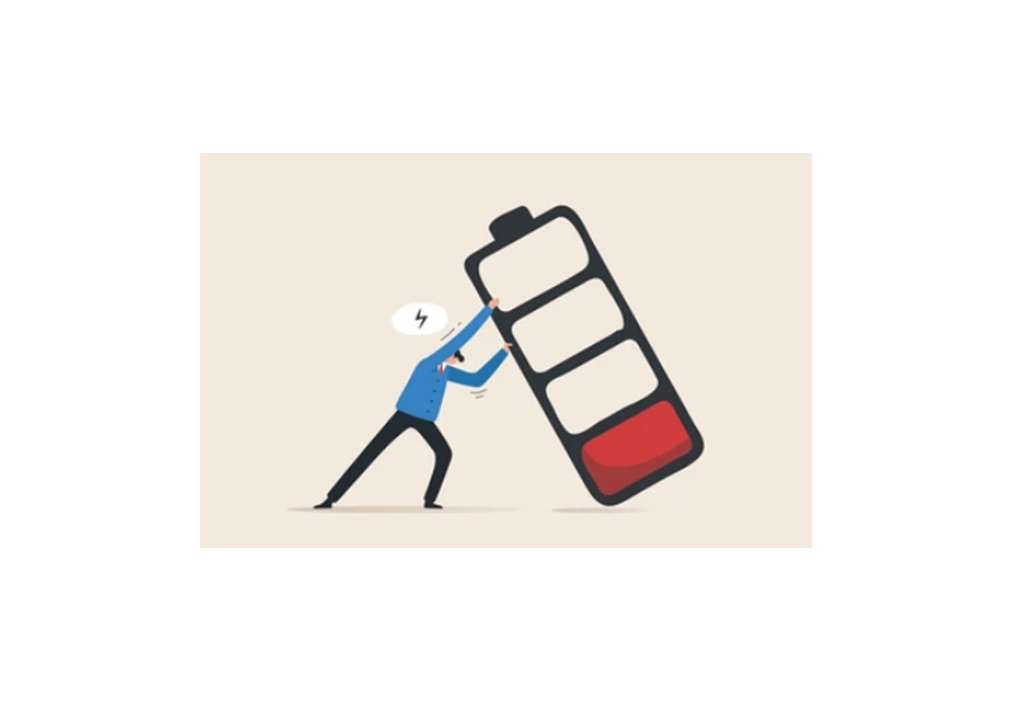
What is Burnout Syndrome?
Burnout syndrome is a condition that is frequently encountered in today's intense and competitive business world and is characterized by physical, emotional and mental exhaustion as a result of excessive stress and pressure that individuals are exposed to in business life. Burnout syndrome, first described by Herbert Freudenberger in the 1970s, is especially common in occupational groups working under high stress, such as health professionals, teachers, social workers and managers.
Symptoms of Burnout Syndrome
Burnout syndrome usually manifests itself in three main dimensions: physical, emotional and mental.
Physical Symptoms
- Chronic Fatigue: Feeling tired all the time, fatigue that does not go away with rest.
- Headaches: Frequent headaches due to stress and tension.
- Sleep Problems: Difficulty falling asleep, waking up frequently or waking up tired in the morning.
- Digestive Problems: Negative effects of stress on the stomach and intestinal system, digestive problems.
- Muscle and Joint Pain: Muscle and joint pains caused by the physical strain of stress.
Emotional Symptoms
- Depression Long-term unhappiness, hopelessness and loss of interest.
- Anxiety: Constant worry, anxiety about the future.
- Irritability: Restlessness, irritability, outbursts of anger.
- Withdrawal: Social isolation, avoidance of human contact.
- Loss of Motivation: Loss of interest and enthusiasm for work and other activities.
Mental Symptoms
- Impaired Concentration Difficulty concentrating, often absent-minded.
- Decision Making Difficulty: Difficulty making even simple decisions.
- Forgetfulness: Memory problems, often forgetting things.
- Negative Thoughts: Negative thoughts about oneself and one's work, feeling of failure.
Causes of Burnout Syndrome
Various factors play a role in the emergence of burnout syndrome. These factors can be caused by personal, work and environmental factors.
Work Related Factors
- High Workload: Long working hours and excessive workload drain a person's energy.
- Unclear Role Definitions: Lack of clarity of duties and responsibilities and uncertainty increase stress.
- Constant Pressure: High performance expectations and constant pressure to succeed.
- Lack of Support: Not receiving enough support and appreciation at work.
- Career Progression: Failure to meet career expectations or failure to advance at work.
Personal Factors
- Perfectionism: Wanting everything to be perfect, fear of making mistakes.
- Inability to Say No: Excessive helpfulness, taking on too much because of the desire to please others.
- Low Self-confidence: Lack of confidence in one's own abilities and skills.
- Internal Conflicts: Incompatibility between personal values and the requirements of the job.
Environmental Factors
- Toxic Work Environment: Competitive, conflictual and negative work atmosphere.
- Work-Life Balance: Inability to balance work and personal life.
- Family and Social Support: Inadequate family and social support systems.
Stages of Burnout Syndrome
Burnout syndrome usually develops in four stages. At each stage, the symptoms become more severe and the person's general health deteriorates.
1. Honeymoon Period
During this period, a person starts work with great enthusiasm, full of high energy and positive emotions. However, this enthusiasm and energy starts to diminish with increasing stress and pressure.
2. Stress Period
As the workload increases and pressures intensify, symptoms of stress begin to emerge. Fatigue, insomnia and decreased performance are the hallmarks of this period.
3. Chronic Stress
Stress symptoms become chronic and permanent. The person begins to experience emotional and physical fatigue. Depression and anxiety symptoms become evident.
4. Burnout
The final stage is complete physical and emotional burnout. The person becomes detached from work and life and may experience serious health problems.
How to Solve Burnout Syndrome?
Various strategies can be applied to cope with and recover from burnout syndrome. These strategies should be both individual and organizational.
Individual Strategies
- Seek Professional Support: Seeking help from a therapist or psychologist is an effective way to overcome burnout syndrome.
- Establishing a Work-Life Balance: It is important to organize working hours and make time for rest and hobbies.
- Stress Management: Stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, breathing exercises are beneficial.
- Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet, regular exercise and adequate sleep play a critical role in maintaining physical and mental health.
- Support Groups: Sharing experiences with others with similar problems provides emotional support.
- Personal Development: It is important to set personal boundaries, learn to say “no” when necessary and develop time management skills.
Organizational Strategies
- Balancing Workload: Distributing the workload of employees fairly, reducing excessive workload.
- Clarifying Role Definitions: Determining the duties and responsibilities of employees in a clear and precise manner.
- Support and Recognition Systems: Appreciating the efforts and achievements of employees and creating a supportive working environment.
- Flexible Working Hours: Offering flexible working hours so that employees can maintain their work-life balance.
- Stress Management Trainings: Providing training to employees on coping with stress and time management.
Although burnout syndrome is an inevitable consequence of modern business life, it can be overcome with awareness and the right interventions. Recognizing oneself, knowing one's limits and seeking professional help when necessary are important steps in this process. At the corporate level, policies and practices that care about the health and happiness of employees play a critical role in preventing and managing burnout syndrome. A healthy mind and body is a basic requirement for a sustainable work and life.
Hashtags
burnout syndrome individual therapy online therapy work life stress pressure relationship
Categories
Actual Other